SEO, short for Search Engine Optimization, is a set of tactics to improve your website’s rankings for important keywords on search engines like Google and Yahoo.
It’s focused on driving organic search traffic to your site via clicks on your listing on the search engine results page (SERP). As opposed to the paid ads at the top of the search results page, organic traffic is completely free, which makes SEO an especially worthwhile investment.
Especially for retailers who want to increase the number of shoppers who come in from search engines. Because if you’re a flower shop and you rank first for “flowers”, then you could see a significant spike in sales from creating a keyword strategy that focused on SEO.
While most of today’s site platforms (like WooCommerce or Shopify) are “SEO-friendly”, there is still a lot you can do to make sure you’re maximizing your ranking potential. And it all starts with your keywords…
Ecommerce SEO: How to Do Keyword Research
Keywords are the building blocks of SEO. These are the terms that represent your products, the ones that you want to be found for when someone searches for them on Google. Before undergoing any kind of site optimization, you must first identify your target keyword list.
Keyword research guidelines:
- Choose keywords that are highly relevant to your business. Opt for slightly broader terms for the category level, and more specific terms for the product detail pages. Stay away from overly broad terms, which are difficult to rank for and tend to bring in lower quality traffic.
- Choose terms that show strong buyer intent. Someone searching for “kitchenware reviews” is still in the research phase, while someone searching for “kitchenware for new apartment” is more likely to be ready to buy.
- Check the keyword search volume. Search volume is the number of times a keyword is searched on in a month. There’s no sense optimizing for a keyword that has little to no search volume. On the flip side, if a keyword has an extremely high search volume and is highly competitive, you may never be able to attain a page 1 ranking. Aim to strike a balance between keyword relevancy, search volume, and competition.
- Use your competitors for keyword inspiration. But beware! Just because a competitor is optimized for a keyword doesn’t mean it’s the right term for you, or that they’ve done their homework in terms of search volume and intent.
Tools for Keyword Research
There are tons of different tools to help you optimize your ecommerce site for search engines. These are some of the industry standards for getting the keyword information you need:
- Google Keyword Tool – Simply type in a keyword and Google’s tool will provide you with related terms and report on monthly search volume, competition level, and CPCs.
- Moz Keyword Explorer – Provides monthly volume, keyword difficulty, organic CTR, keyword suggestions, and more. You can also search by domain, to see what keywords your competitors are ranking for. Note: the free version limits the number of queries you can research.
- Serpstat – Similar functionality to Moz, Serpstat also includes pay per click info so you can see what ads your competitors are running and the CPCs they’re paying.
Ecommerce SEO: How to Do On-Site Optimization
Optimizing your site for search engines involves making changes to tagging, content, and architecture to clearly signify to the engines what your site, and each page within it, is about. The end goal is to convince the search engines that a page on your site is the best resource for a related search query, so that it will rank you at the top of the search results.
Before you do anything else, make sure your site complies with these 5 must-haves:
- Google gives preference to sites that are secure (use https in the URL). If you haven’t already, be sure to make the switch to the https protocol (and 301 redirect the http version to the https version. Have your web team or hosting provider help you with this or do a search for “how to 301 redirect <insert platform name>” for instructions).
- Mobile friendly. Because of the prevalence of mobile usage, Google is slowly rolling out a mobile-first index. This means that it will base its rankings on the mobile version of your site. If you have a responsive site, you’re in the clear. If you have a mobile version of your site (like m.yoursite.com), you’ll want to make sure that the content is represented in the mobile version. If your site isn’t mobile-friendly, you’ll want to make it responsive ASAP.
- Site speed is an important part of the ranking algorithm. Check your load time here and aim for a score of 85/100 or better.
- Simple. Make sure your site structure is simple and clear, with no page more than 3 clicks away from the home page.
- Unique content. Google is not a fan of duplicate content and having it on your site can negatively impact your rankings. Product variations, the same product available in multiple categories, and other factors can lead to duplicate content on ecommerce sites. Be sure to use canonical tags to tell the search engines the “canon” or primary URL that they should assign all search value to.
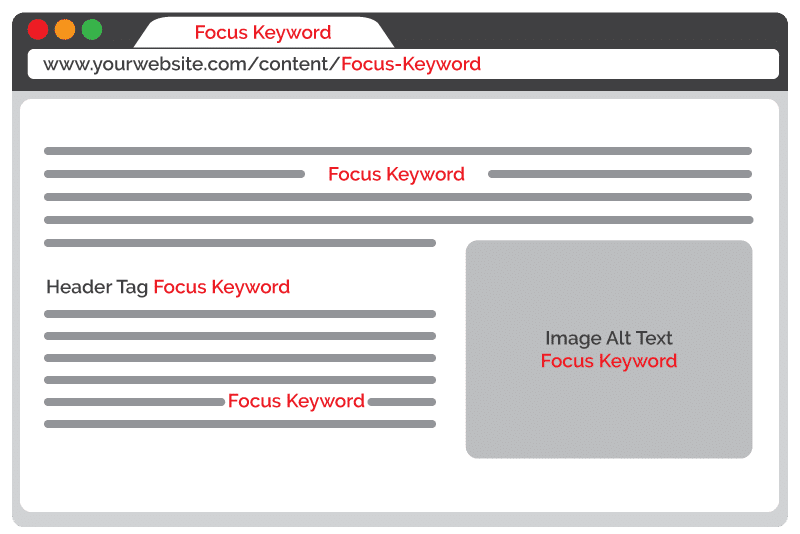
Once you’ve addressed the big five, it’s time to tackle category and product page optimization. Map your keywords to your category and product pages. Stick to one main keyword per page – no keyword stuffing! Then, add keyword mentions to the pages, in all of the following places, if possible:
- URL: The ideal URL should be short, easy to read, and free from unnecessary letters, numbers, and characters.
- Title tag: The title tag is what shows in the page tab at the top of the browser. Try to include your keyword as close to the beginning of the title tag as possible and stick to around 70 characters if possible to avoid truncation in the SERPs.
- H1 tag: The H1 tag is typically the headline on the page. If it makes sense, use the keyword here, too.
- Image alt text: Alt text is used to describe what an image is about – useful for the vision impaired and for search engine spiders. Include your keyword here, too, if it makes sense with the image.
- Meta description: This is what search engines often use for the summary shown underneath the listing title in the SERPs. It doesn’t influence rankings per se, but searchers like to see their query repeated here, and a well-written description can encourage click through.
- Body copy: The general rule of thumb is to use the keyword 2-3 times per 200-300 words of copy. It is important NOT to stuff in as many mentions as possible – this will trigger a spam flag with the search engines. Your copy should read naturally, and the keywords shouldn’t feel forced. Don’t be afraid to use variations of the keyword – search engines are very good at linking semantically related terms.
Additional SEO Considerations for Product Pages
To optimize product pages, you’ll want to use the keyword in all the places mentioned above, and also consider:
- Adding reviews. Shoppers rely on reviews heavily to make their decision purchases, and from an SEO standpoint, they also help add content and keyword mentions to your page. If you don’t already include them, you can add reviews easily with a service like Yotpo or PowerReviews.
- Beefing up content. Product pages on other sites that are more content-heavy are more likely to outrank you. To stay competitive, aim for 500-1000 words, by including content around product description, features, benefits, specifications, materials, and use cases. Rich media like photos and video can help even more.
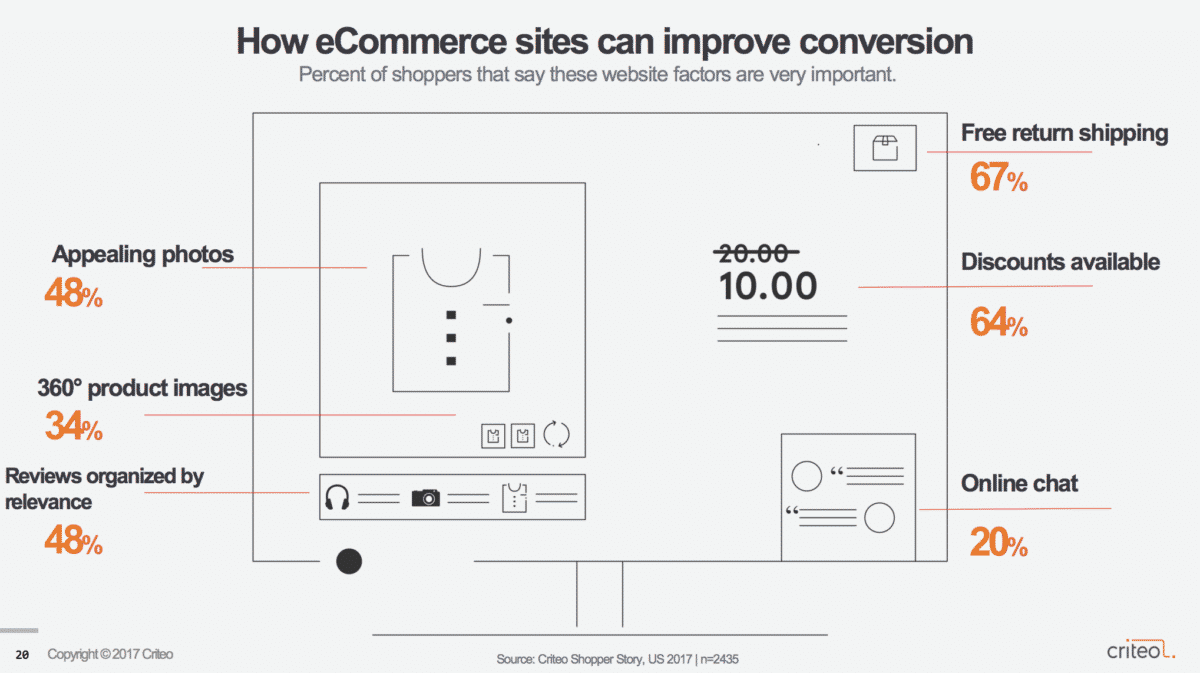
- Optimize for conversions. According to our Shopper Story report, 48% of shoppers say that appealing photos are important, and 34% want to see 360° product views. Of course, free shipping, discounts, and reviews were hugely important, too.
Ecommerce SEO: How to Do Local SEO
Retailers with brick-and-mortar locations will also want to optimize the presence of each store on search engines. You can generate local SEO by following these steps:
- Claim your Google My Business Listing for each location. This is what is displayed in the local results, below the map.
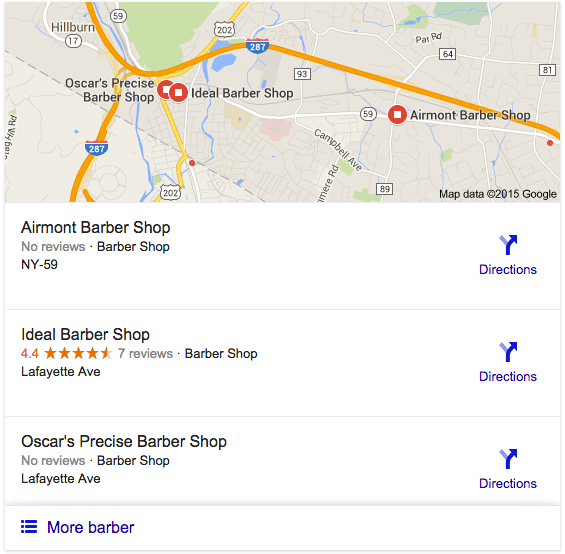
- Make your Google My Business Listing as robust as possible: include images, website address, hours, etc.
- Ensure your location(s) has citations in all the major online directories (Yelp, YellowPages, SuperPages, etc.).
- Take care to be consistent with your NAP (Name, Address, Phone Number) across all of the listings. Services like BrightLocal or Moz Local can help you manage this process.
Ecommerce SEO: How to Do Link Optimization
A huge part of the search engine ranking algorithm is the quantity and quality of inbound links to your site, as well as the amount of internal linking within your site.
“Inbound links” are links that are created on different websites and point back to your own site. To the search engines, inbound links are proof of your credibility — if lots of others are linking to you, then you must be a legitimate resource.
“Internal links” are the links that link between pages on your own website. A strong internal linking structure helps spread the link juice from high authority pages throughout the site and makes it easier for the search engines to discover related content.
Here’s how to boost your link profile:
- Cross-link between product pages, and if you have a blog, cross-link between your blog posts and category and product pages as appropriate.
- Link on keywords and/or descriptive anchor text rather than “learn more”, or “click here”.
- Write educational content around the products that you sell – tips, style guides, how-to series, etc. Make it useful and interesting so that others feel compelled to link to it and share it.
- Use your keywords in your social posts and encourage click throughs to your site content.
- Make the most of partnerships you have, groups you’re a member of, charities you support, etc. – if they’re not already linking to you, request that they add a link to your site.
- Partner with top social media influencers in your category to reach a wider audience.
Ready to dominate the SERPs? Let’s sum up the 4 key SEO tactics:
- Identify your keywords. Aim to strike a balance between keyword relevancy, search volume, intent, and competition.
- Carry out on-site optimization: Address the 5 must-haves (secure, mobile-friendly, fast, simple, unique), and add keywords to the 6 main elements of your category and product pages.
- If you have a physical store, don’t forget local SEO. Claim your Google My Business Listing and build citations on the top online directories.
- Optimize your link profile. Enhance your internal links and build external links from other high-quality sites.